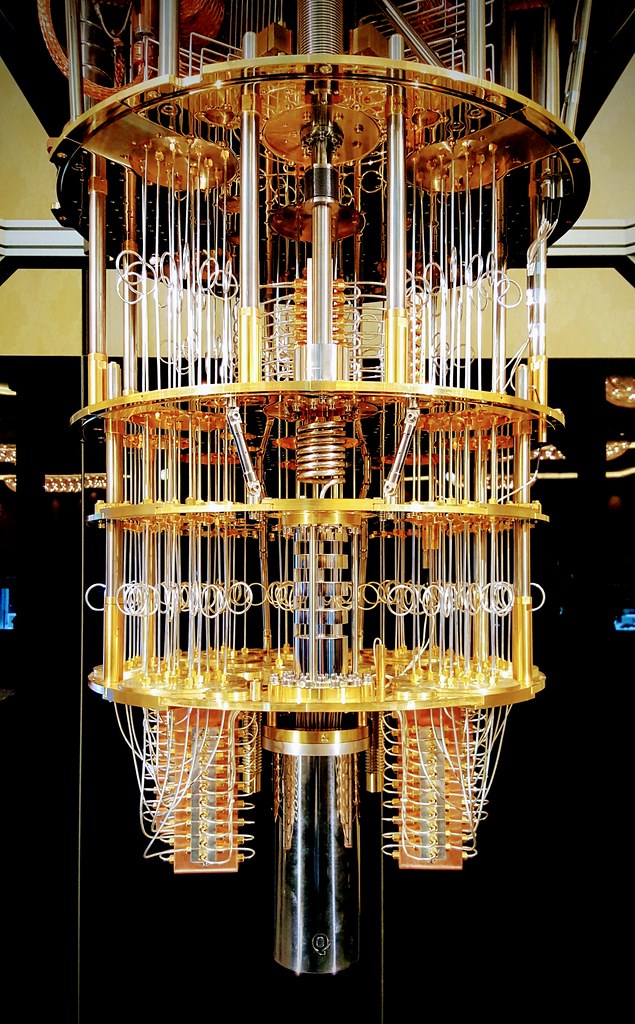
Quantum computers are a type of computer that use quantum mechanics to store and process data. Unlike classical computers that use binary digits (bits) to represent information as either 0 or 1, quantum computers use quantum bits (qubits) that can exist in a state of 0, 1, or both simultaneously (a superposition). This allows quantum computers to perform certain tasks much faster than classical computers.
One of the most promising applications of quantum computers is in the field of cryptography, where they can be used to create unbreakable codes. They can also be used for optimization problems, such as finding the shortest route between multiple destinations, or for simulating complex chemical reactions that would be difficult to simulate on classical computers.
However, quantum computers are still in the early stages of development and are currently limited in their capabilities due to issues with noise and error correction. As a result, they are not yet practical for most real-world applications. But as research continues and technology advances, it is likely that quantum computers will play an increasingly important role in fields such as finance, materials science, and drug discovery.
Another potential application of quantum computers is in the field of machine learning. Quantum machine learning algorithms could potentially process vast amounts of data much faster than classical algorithms, allowing for more accurate predictions and more efficient decision-making.
Research into quantum computing is currently being conducted by many academic and industrial organizations around the world. Major players in the field include IBM, Google, Microsoft, and Intel. In India, research into quantum computing is being conducted at institutions such as the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) in Bombay and the Centre for Quantum Technologies at the Indian Institute of Science Education and Research (IISER) in Mohali.
These research teams are exploring ways to overcome the challenges associated with noise and error correction in quantum computing, as well as developing new quantum algorithms and hardware. The research team leaders in India include Dr. Animesh Datta, Dr. Arvind and Dr. Apoorva Patel, among others.
As the field of quantum computing continues to advance, it is likely that we will see more breakthroughs and applications emerging. While the technology is still in its infancy, its potential to revolutionize computing and solve previously unsolvable problems make it a fascinating area of research and development.
The 10-qubit quantum computer developed by the Centre for Development of Advanced Computing in Pune likely uses superconducting qubits, which are one of the most promising technologies for building practical quantum computers. Superconducting qubits are made of tiny loops of superconducting wire and can be used to store and process quantum information. They are highly sensitive to noise and other environmental factors, which can cause errors in calculations, so researchers are working to develop ways to reduce these sources of error and improve the stability of the qubits. Superconducting qubits are just one of several technologies being explored for building quantum computers, and researchers are also investigating other approaches such as ion trap and topological qubits. Each technology has its own advantages and challenges, and it is likely that a combination of these technologies will be needed to build practical and scalable quantum computers in the future.
The Indian government has shown a growing interest in quantum technologies in recent years, recognizing the potential impact they could have on a wide range of industries and fields. In 2018, the government announced the launch of the National Mission on Quantum Technologies and Applications, which aims to accelerate research and development in quantum technologies in India. The mission is being led by the Department of Science and Technology, and it involves collaboration with various research institutions and industry partners.
The government has also established several initiatives to support quantum research and development in India. For example, the Department of Science and Technology has provided funding for several quantum research centers, including the Centre for Quantum Technologies at the Indian Institute of Science Education and Research in Mohali, and the Centre for Excellence in Quantum Computing and Quantum-Enabled Technologies at the Indian Institute of Technology in Kanpur. Additionally, the government has provided funding for quantum research and development projects in various fields, such as healthcare, agriculture, and defense.
Overall, the Indian government’s increasing focus on quantum technologies is a reflection of the growing global interest in this field and the potential it holds for advancing science, technology, and innovation. By investing in quantum research and development, the government is helping to position India as a key player in this exciting and rapidly evolving field.
